在本文中讨论的一些shell特殊参数是:,@,#,,!
示例1:使用 和@ 来扩展位置参数
本实例脚本中使用和@参数:
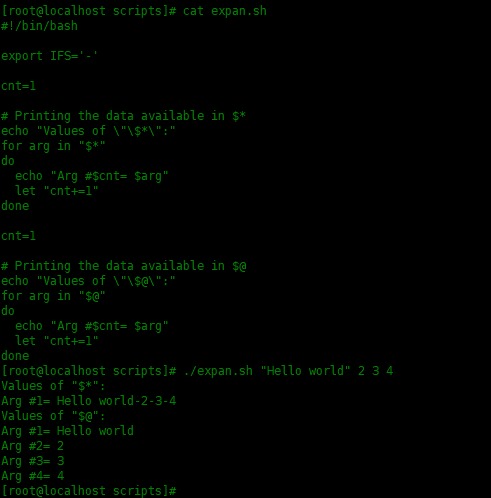
[root@localhost scripts]# vim expan.sh
#!/bin/bash
export IFS='-'
cnt=1
# Printing the data available in $*
echo "Values of \"\$*\":"
for arg in "$*"
do
echo "Arg #$cnt= $arg"
let "cnt+=1"
done
cnt=1
# Printing the data available in $@
echo "Values of \"\$@\":"
for arg in "$@"
do
echo "Arg #$cnt= $arg"
let "cnt+=1"
done
下面是运行结果:
[root@localhost scripts]# ./expan.sh "Hello world" 2 3 4
Values of "$*":
Arg #1= Hello world-2-3-4
Values of "$@":
Arg #1= Hello world
Arg #2= 2
Arg #3= 3
Arg #4= 4
-
export IFS='-'表示使用” – “表示内部字段分隔符。 -
当打印参数 $*的每个值时,它只给出一个值,即是IFS分隔的整个位置参数。 -
而 $@将每个参数作为单独的值提供。
示例2:使用$#统计位置参数的数量
$#是特殊参数,它可以提更脚本的位置参数的数量:
[root@localhost scripts]# vim count.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -lt 2 ]
then
echo "Usage: $0 arg1 arg2"
exit
fi
echo -e "\$1=$1"
echo -e "\$2=$2"
let add=$1+$2
let sub=$1-$2
let mul=$1*$2
let div=$1/$2
echo -e "Addition=$add\nSubtraction=$sub\nMultiplication=$mul\nDivision=$div\n"
下面是运行结果:
[root@localhost scripts]# ./count.sh
Usage: ./count.sh arg1 arg2
[root@localhost scripts]# ./count.sh 2314 15241
$1=2314
$2=15241
Addition=17555
Subtraction=-12927
Multiplication=35267674
Division=0
脚本中if [ $# -lt 2 ]表示如果位置参数的数量小于2,则会提示”Usage: ./count.sh arg1 arg2″。
**
**
示例3:与过程相关的参数 $$和$!
参数$$将给出shell脚本的进程ID。$!提供最近执行的后台进程的ID,下面实例是打印当前脚本的进程ID和最后一次执行后台进程的ID:
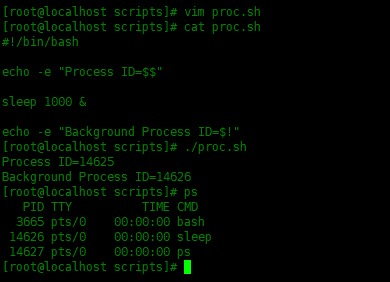
[root@localhost scripts]# vim proc.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo -e "Process ID=$$"
sleep 1000 &
echo -e "Background Process ID=$!"
下面是执行的结果:
[root@localhost scripts]# ./proc.sh
Process ID=14625
Background Process ID=14626
[root@localhost scripts]# ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
3665 pts/0 00:00:00 bash
14626 pts/0 00:00:00 sleep
14627 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
以上就是良许教程网为各位朋友分享的Linu系统相关内容。想要了解更多Linux相关知识记得关注公众号“良许Linux”,或扫描下方二维码进行关注,更多干货等着你 !



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
 支付宝扫一扫打赏
支付宝扫一扫打赏

.png)
