多线程编程是现代编程中不可或缺的一部分,可以提高程序的性能和响应速度。然而在Linux系统下,多线程编程的实现却比较复杂,特别是对于线程锁的使用和管理,更是需要我们细致的掌握。
在编程中,引入了对象互斥锁的概念,来保证共享数据操作的完整性。每个对象都对应于一个可称为” 互斥锁” 的标记,这个标记用来保证在任一时刻,只能有一个线程访问该对象。Linux实现的互斥锁机制包括POSIX互斥锁和内核互斥锁,本文主要讲POSIX互斥锁,即线程间互斥锁。
信号量用在多线程多任务同步的,一个线程完成了某一个动作就通过信号量告诉别的线程,别的线程再进行某些动作(大家都在sem_wait的时候,就阻塞在 那里)。而互斥锁是用在多线程多任务互斥的,一个线程占用了某一个资源,那么别的线程就无法访问,直到这个线程unlock,其他的线程才开始可以利用这 个资源。比如对全局变量的访问,有时要加锁,操作完了,在解锁。有的时候锁和信号量会同时使用的”
也就是说,信号量不一定是锁定某一个资源,而是 流程上的概念,比如:有A,B两个线程,B线程要等A线程完成某一任务以后再进行自己下面的步骤,这个任务并不一定是锁定某一资源,还可以是进行一些计算 或者数据处理之类。而线程互斥量则是“锁住某一资源”的概念,在锁定期间内,其他线程无法对被保护的数据进行操作。在有些情况下两者可以互换。
两者之间的区别:
作用域
信号量 : 进程间或线程间(linux仅线程间)
互斥锁 : 线程间
上锁时
信号量 : 只要信号量的value大于0,其他线程就可以sem_wait成功,成功后信号量的value减一。若value值不大于0,则sem_wait阻塞,直到sem_post释放后value值加一。一句话,信号量的value>=0 。
互斥锁 : 只要被锁住,其他任何线程都不可以访问被保护的资源。如果没有锁,获得资源成功,否则进行阻塞等待资源可用。一句话,线程互斥锁的vlaue可以为负数 。
多线程
线程是计算机中独立运行的最小单位,运行时占用很少的系统资源。与多进程相比,多进程具有多进程不具备的一些优点,其最重要的是:对于多线程来说,其能够比多进程更加节省资源。
线程创建
在Linux中,新建的线程并不是在原先的进程中,而是系统通过一个系统调用clone()。该系统copy了一个和原先进程完全一样的进程,并在这个进程中执行线程函数。
在Linux中,通过函数pthread_create()函数实现线程的创建:
pthread_create()
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,void *(*st
其中:
thread表示的是一个pthread_t类型的指针;
attr用于指定线程的一些属性;
start_routine表示的是一个函数指针,该函数是线程调用函数;
arg表示的是传递给线程调用函数的参数。
当线程创建成功时,函数pthread_create()返回0,若返回值不为0则表示创建线程失败。对于线程的属性,则在结构体pthread_attr_t中定义。
线程创建的过程如下所示:
#include
#include
#include
#include
void* thread(void *id){
pthread_t newthid;
newthid = pthread_self();
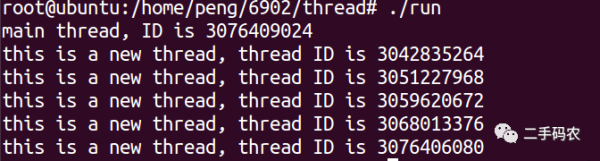
printf("this is a new thread, thread ID is %u\n", newthid);
return NULL;
}
int main(){
int num_thread = 5;
pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * num_thread);
printf("main thread, ID is %u\n", pthread_self());
for (int i = 0; i if (pthread_create(&pt[i], NULL, thread, NULL) != 0){
printf("thread create failed!\n");
return 1;
}
}
sleep(2);
free(pt);
return 0;
}
在上述代码中,使用到了pthread_self()函数,该函数的作用是获取本线程的线程ID。在主函数中的sleep()用于将主进程处于等待状态,以让线程执行完成。最终的执行效果如下所示:
那么,如何利用arg向子线程传递参数呢?其具体的实现如下所示:
#include
#include
#include
#include
void* thread(void *id){
pthread_t newthid;
newthid = pthread_self();
int num = *(int *)id;
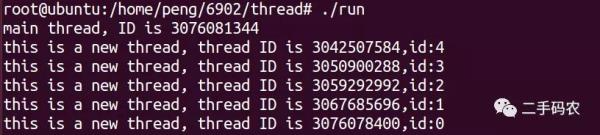
printf("this is a new thread, thread ID is %u,id:%d\n", newthid, num);
return NULL;
}
int main(){
//pthread_t thid;
int num_thread = 5;
pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * num_thread);
int * id = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_thread);
printf("main thread, ID is %u\n", pthread_self());
for (int i = 0; i if (pthread_create(&pt[i], NULL, thread, &id[i]) != 0){
printf("thread create failed!\n");
return 1;
}
}
sleep(2);
free(pt);
free(id);
return 0;
}
其最终的执行效果如下图所示:
如果在主进程提前结束,会出现什么情况呢?如下述的代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
void* thread(void *id){
pthread_t newthid;
newthid = pthread_self();
int num = *(int *)id;
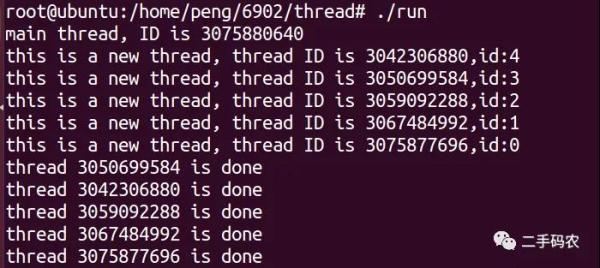
printf("this is a new thread, thread ID is %u,id:%d\n", newthid, num);
sleep(2);
printf("thread %u is done!\n", newthid);
return NULL;
}
int main(){
//pthread_t thid;
int num_thread = 5;
pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * num_thread);
int * id = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_thread);
printf("main thread, ID is %u\n", pthread_self());
for (int i = 0; i if (pthread_create(&pt[i], NULL, thread, &id[i]) != 0){
printf("thread create failed!\n");
return 1;
}
}
//sleep(2);
free(pt);
free(id);
return 0;
}
此时,主进程提前结束,进程会将资源回收,此时,线程都将退出执行,运行结果如下所示:
线程挂起
在上述的实现过程中,为了使得主线程能够等待每一个子线程执行完成后再退出,使用了free()函数,在Linux的多线程中,也可以使用pthread_join()函数用于等待其他线程,函数的具体形式为:
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
函数pthread_join()用来等待一个线程的结束,其调用这将被挂起。
一个线程仅允许一个线程使用pthread_join()等待它的终止。
如需要在主线程中等待每一个子线程的结束,如下述代码所示:
#include
#include
#include
#include
void* thread(void *id){
pthread_t newthid;
newthid = pthread_self();
int num = *(int *)id;
printf("this is a new thread, thread ID is %u,id:%d\n", newthid, num);
printf("thread %u is done\n", newthid);
return NULL;
}
int main(){
int num_thread = 5;
pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * num_thread);
int * id = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_thread);
printf("main thread, ID is %u\n", pthread_self());
for (int i = 0; i if (pthread_create(&pt[i], NULL, thread, &id[i]) != 0){
printf("thread create failed!\n");
return 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i return 0;
}
最终的执行效果如下所示:
注:在编译的时候需要链接libpthread.a:
g++ xx.c -lpthread -o xx
互斥锁mutex
多线程的问题引入
多线程的最大的特点是资源的共享,但是,当多个线程同时去操作(同时去改变)一个临界资源时,会破坏临界资源。如利用多线程同时写一个文件:
#include
#include
const char filename[] = "hello";
void* thread(void *id){
int num = *(int *)id;
// 写文件的操作
FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "a+");
int start = *((int *)id);
int end = start + 1;
setbuf(fp, NULL);// 设置缓冲区的大小
fprintf(stdout, "%d\n", start);
for (int i = (start * 10); i "%d\t", i);
}
fprintf(fp, "\n");
fclose(fp);
return NULL;
}
int main(){
int num_thread = 5;
pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * num_thread);
int * id = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_thread);
for (int i = 0; i if (pthread_create(&pt[i], NULL, thread, &id[i]) != 0){
printf("thread create failed!\n");
return 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i return 0;
}
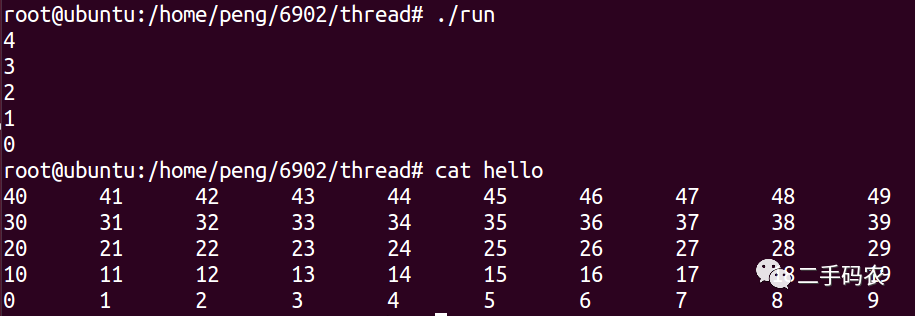
执行以上的代码,我们会发现,得到的结果是混乱的,出现上述的最主要的原因是,我们在编写多线程代码的过程中,每一个线程都尝试去写同一个文件,这样便出现了上述的问题,这便是共享资源的同步问题,在Linux编程中,线程同步的处理方法包括:信号量,互斥锁和条件变量。
互斥锁
互斥锁是通过锁的机制来实现线程间的同步问题。互斥锁的基本流程为:
初始化一个互斥锁:pthread_mutex_init()函数
加锁:pthread_mutex_lock()函数或者pthread_mutex_trylock()函数
对共享资源的操作
解锁:pthread_mutex_unlock()函数
注销互斥锁:pthread_mutex_destory()函数
其中,在加锁过程中,pthread_mutex_lock()函数和pthread_mutex_trylock()函数的过程略有不同:
当使用pthread_mutex_lock()函数进行加锁时,若此时已经被锁,则尝试加锁的线程会被阻塞,直到互斥锁被其他线程释放,当pthread_mutex_lock()函数有返回值时,说明加锁成功;
而使用pthread_mutex_trylock()函数进行加锁时,若此时已经被锁,则会返回EBUSY的错误码。
同时,解锁的过程中,也需要满足两个条件:
解锁前,互斥锁必须处于锁定状态;
必须由加锁的线程进行解锁。
当互斥锁使用完成后,必须进行清除。
有了以上的准备,我们重新实现上述的多线程写操作,其实现代码如下所示:
#include
#include
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
const char filename[] = "hello";
void* thread(void *id){
int num = *(int *)id;
// 加锁
if (pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex) != 0){
fprintf(stdout, "lock error!\n");
}
// 写文件的操作
FILE *fp = fopen(filename, "a+");
int start = *((int *)id);
int end = start + 1;
setbuf(fp, NULL);// 设置缓冲区的大小
fprintf(stdout, "%d\n", start);
for (int i = (start * 10); i "%d\t", i);
}
fprintf(fp, "\n");
fclose(fp);
// 解锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return NULL;
}
int main(){
int num_thread = 5;
pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t) * num_thread);
int * id = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * num_thread);
// 初始化互斥锁
if (pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL) != 0){
// 互斥锁初始化失败
free(pt);
free(id);
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i if (pthread_create(&pt[i], NULL, thread, &id[i]) != 0){
printf("thread create failed!\n");
return 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i return 0;
}
最终的结果为:
本文详细讲解了Linux下多线程编程中线程锁的使用方法和技巧,包括互斥锁、读写锁、条件变量等,以及对于每种锁的优缺点和适用场景的介绍。同时,我们也探讨了一些常见的线程安全编程问题,如死锁、活锁和饥饿等,并给出了相应的解决方案。通过本文的学习,您将能够更好地运用线程锁解决多线程编程中的问题,提高程序的可靠性和稳定性。
以上就是良许教程网为各位朋友分享的Linu系统相关内容。想要了解更多Linux相关知识记得关注公众号“良许Linux”,或扫描下方二维码进行关注,更多干货等着你 !




 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
 支付宝扫一扫打赏
支付宝扫一扫打赏

.png)
